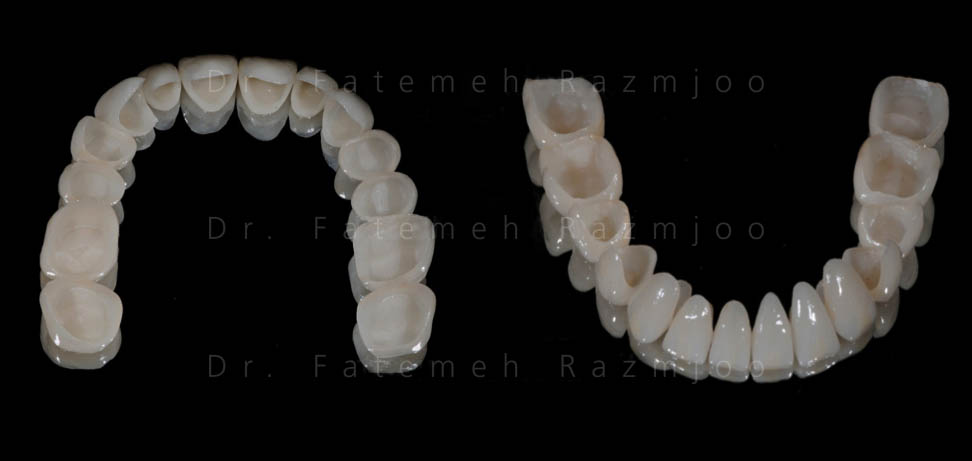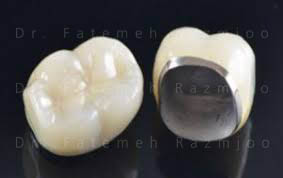
An ideal therapy plan must consider an accurate examination of the structure of the remaining teeth to determine whether they need to be treated by a restorative point of view, and especially if they may be a valid base for the prosthetic rehabilitation. The restorations, built in the laboratory, have the task of restoring the morphology and the shape of the teeth, in order to satisfy both the aesthetic and functional necessities of the patient.
The prosthesis must be also biologically well integrated and must respect both the gingival tissues and the pulp organ during these phases: tooth preparation, impression taking, positioning and cementation of the provisional and final restorations.
The clinician can use various rehabilitation modalities: from the most simple ones, like the mucosa-supported removable prosthesis, to the most complex ones, like the fixed rehabilitation with crowns covering the natural abutments.
The loss of teeth or the lack of reliability in the existing natural elements lead the clinician and the patient to decide, most of the time, to extract the teeth, and prosthetic solutions based on osseointegrated implants that can effectively replace the missing teeth.
In any prosthetic rehabilitation, both limited to an area of the oral cavity or extended to the whole mouth, a periodic and attentive monitoring of the performed rehabilitation is very important for the maintenance over time of the restorations, as well as a careful and systematic check of the patient’s oral hygiene.